On today's episode of Feudal Future hosts Joel Kotkin and Marshall Toplansky are joined by guest Kyle Harper, a professor of classics at the University of Oklahoma. Their discussion looks to the past, particularly the fall of Rome to help understand the problems of today. Kyle’s book, The Fall of Rome takes a look at infectious disease as part of the destruction of Rome.
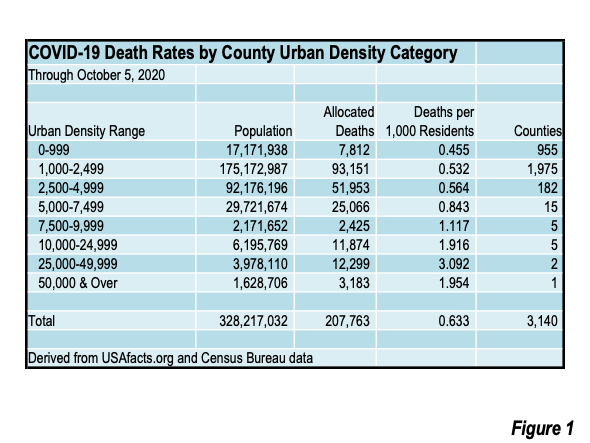
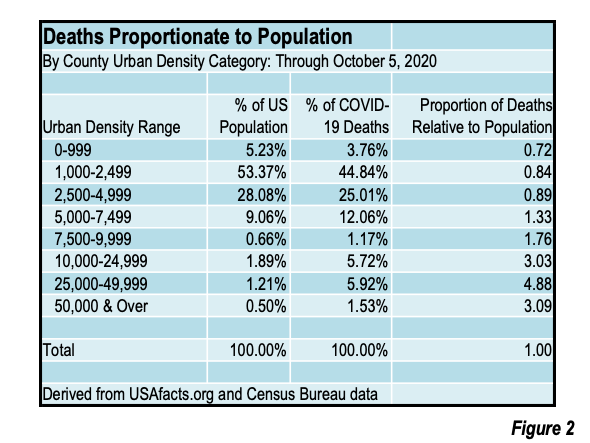
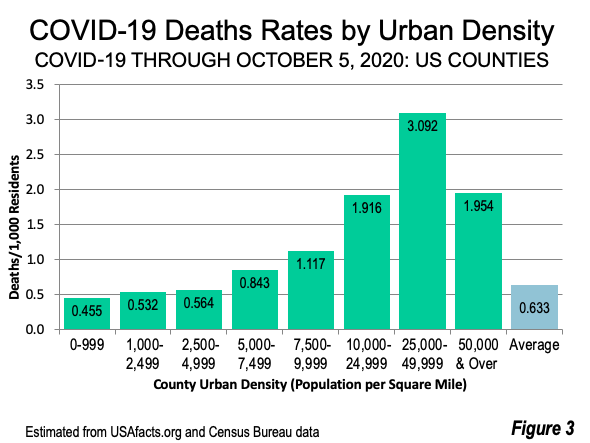
Second century Romans lived in an urban society with regular intercontinental exchange that utilized the Indian Ocean, Silk Roads, and the Sahara. There’s also a randomness to evolutionary events that combine with the risk factors of globalization that create viruses that can spread rapidly across humans. While density can be a factor in the spreading of infectious disease, given the interconnectedness of the global economy, density makes less of a difference today than it may have in the past. Kyle stresses that both density and connectivity matter. To the disease, he explains, we’re just a host, anything we do that changes their evolutionary prospects affects them. Every parasite has to combat healthy immune systems and travel from host to host. Respiratory pathogens take advantage of the fact that we live in such a connected way.
From studying medieval and Roman problems, there are certainly lessons to take away for the modern pandemic and political age. Enlightenment science and the rise of germ theory and public health are part of lifting us from the oppression of infectious disease. We don’t learn from their handling of the disease, because they didn’t have the knowledge, science, or infrastructure to respond well. However, it can help us to be aware of threats and the biological realities of our universe. Historically, the COVID was bound to happen, will happen again, and may be much worse. Kyle stresses that one take away should be learning from this pandemic and becoming more prepared for another infectious disease outbreak in the future. It’s not just science that plays a role in pandemic response, it’s also social and behavioral programs and leadership that impacts the outcomes.
More podcast episodes & show notes at JoelKotkin.com
Watch Episode on Youtube
Related:
Learn more about the Feudal Future podcast.
Learn more about Marshall Toplansky.
Learn more about Joel Kotkin.
Learn about Kyle Harper.