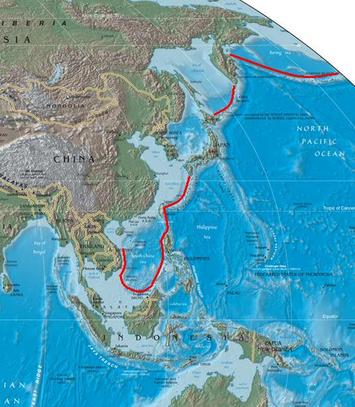
When China’s navy looks beyond its coastal waters, which it increasingly does, it sees a kind of Great Wall. The Chinese call this the “First Island Chain,” a line of islands, some small, others huge, extending from the Japan archipelago to the north, the Ryuku island chain past Taiwan, and the Philippines to the south. The waters within this arc are considered an integral part of China itself.
Increasingly, China’s sailors are penetrating this barrier through various choke points to gain access to the broader Western Pacific Ocean. In late November, a large formation of Chinese long-range bombers and support craft passed through the gap between Okinawa and the island of Miyako, the so-called “Miyako Channel".
The Miyako Channel is strategically vital for China because it is one of the few international waterways through which the Chinese navy and air can access the Pacific Ocean without violating somebody’s space. It is also located close to the Japanese-controlled Senkaku islands which are also claimed by China.
The first time a Chinese H-6K bomber passed through the channel was September, 2013; the first multi-plane formation to use this passageway was in May this year, and late this year an unusually large formation of eight bombers and support aircraft passed through the gap, flew around the Pacific, and then returned to home base through the channel.
The H-6K is a modified and much improved version of an old Soviet Tu-22 bomber, known as a “Badger”. It has been configured to hold cruise missiles under its wings or in its bomb bay. The planes reportedly flew about 620 miles into the Pacific before returning to their home base near Shanghai.
Both the Chinese navy and the air force are learning to conduct extended maritime operations far from home waters and into the wider Western Pacific. Of course, China has maintained a permanent, rotating flotilla of two destroyers and a supply ship in the waters off the coast of Somalia and the Gulf of Aden since 2009. Unlike Japan, it does not have a permanent base in that region, although it is seeking one.
In March, 2014, two Chinese warships docked at Abu Dhabi, the first time a Chinese fleet had made a port call on the Arabian Peninsula since the days of the Treasure Ships of Admiral Zheng He. In 2013, the Chinese navy made its first goodwill visit to South America, and it stationed a guided missile frigate in the Mediterranean to help escort ships removing chemical weapons from Syria.
These missions are not war fighting, but the ships have enhanced capabilities for operating in seas far from home. They have gained experience in coordinating with other naval services on anti-piracy patrol, and exercised with other navies, including those of South Korea and Pakistan.
In the summer of 2013 a Chinese naval flotilla passed through the Soyu Strait, which separates Hokkaido from the southern tip of Russia’s Kurile islands; they returned to their home base through the Miyako Channel. The People’s Daily trumpeted this maneuver as if it were a major triumph. Never mind that these narrow waters are international passageways or that they could easily be closed off if the Japanese decided to do so.
China routinely conducts naval and air exercises beyond the First Island Chain as far away as the Philippine Sea, and the number of Chinese naval flotillas passing through the First Island Chain has increased significantly in recent years. There were two in 2008 and 2009, four in 2010, five in 2011, and eleven in 2012. In 2012 surface combatants were deployed seven times to the Philippine Sea; they were deployed nineteen times in 2013. The Maneuver-5 exercise in the Philippine Sea involved units from all three of China’s fleets, its largest open-ocean exercise to date.
The Chinese navy has now penetrated all of the Western Pacific choke points along the chain, from the Tsuruga Strait separating Hokkaido from Honshu in northern Japan to the Bashi Strait separating Taiwan from the Philippines and the Sunda Strait in Indonesia. In October, 2012 a flotilla exited the East China Sea through the narrow passage way between Taiwan and Japan’s Yonaguna island in the Ryukyu chain (where the Japanese army has constructed a surveillance radar).
This is thought to have been a signal from Beijing of displeasure over Tokyo’s decision to buy the Senkaku islands a month earlier. Later, two Sovremnny Class destroyers and two frigates exited the chain through the Miyako Strait and returned via the waters separating Yonaguna from Taiwan.
The navy has steadily progressed from a handful of vessels, to multi-fleet (i.e. elements from all three of China’s fleets), to combined operations with submarines, drones and long-range bombers. Not only does China maintain a permanent anti-piracy force in the Indian Ocean, it now routinely conducts naval exercises and operates beyond the First Island Chain, says the US National Defense University.
This year China was invited to participate in the Rimpac exercise in waters near Hawaii. It sent a destroyer, but also an intelligence-gathering ship, making it possibly the first time a nation spied on an exercise in which it was a participant.
When queried as to its purpose and intentions of these missions, Beijing has a standard reply: “The training is in line with the relevant international practices and is not aimed at any one country or target and poses no threat to any country or region.”
In June, 2015, Beijing issued a white paper on its defense priorities in which it stated what has been obvious to any naval planner paying attention: that China's naval interests are no longer limited to its coastline, but span the globe. “The traditional mentality [going back to Mao Zedong] that the land outweighs the seas must be abandoned,” the paper states.
That the Chinese navy will enhance its capabilities for “open seas protection” just puts into words what is actually happening. The white paper leaves little doubt that China is intent on transforming itself into a modern maritime power, capable of challenging Japan or the US in Asia and elsewhere.
Todd Crowell is the author of The Coming War, published by Amazon as a Kindle Single.
First Island Chain (perimeter marked in red) map by Suid-Afrikaanse (GFDL) via Wikimedia Commons












