
Teleworking (also known as telecommuting) has taken flight as a global trend. During July of 2002, European Union collectively decided on a shared framework agreement on telework, which regulates issues such as employment and working conditions, health and safety, training, and the collective rights of teleworkers. Following suit, the American the Telework Enhancement Act of 2010 served as a rallying call for federal agencies to encourage “work-at-home” employees. In the same year officials in China, eager to reduce gross national carbon emissions, chose the province of Hubei to undergo the country’s first telecommuting pilot program
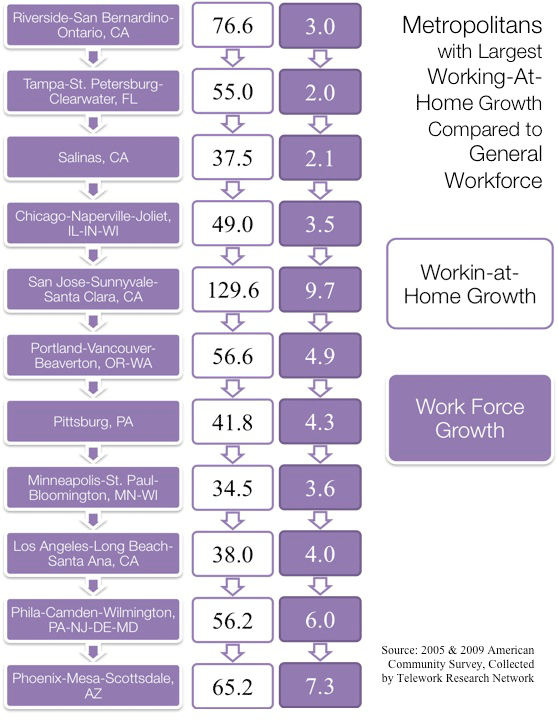
In the United States, telecommuting is on the clear increase. Data from the American Community Survey estimate that the working at home population grew 61% between 2005 and 2009. The biggest increases in teleworking population compared to workforce was in Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario, CA while the metro with the highest growth in teleworking was San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA.
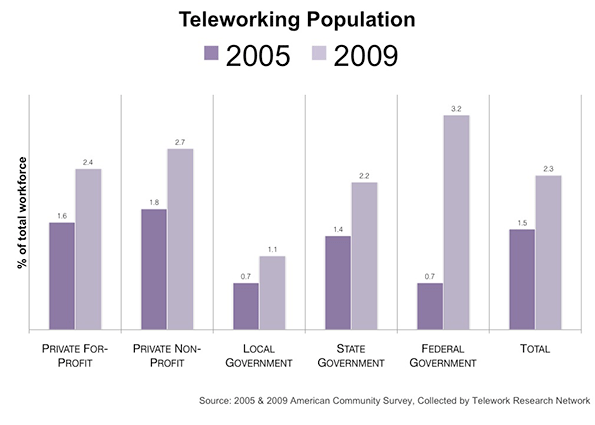
Is the trend to telecommuting comparable between the private and public sectors? The 2009 American Community Survey gives a snapshot of the work-at-home population by class of worker in the years 2005 and 2009. Although the rise of teleworkers is across both sectors, a surge in government teleworkers indicates the public sector, notably the federal government, has made a huge effort keep staff at home to cut administrative costs.
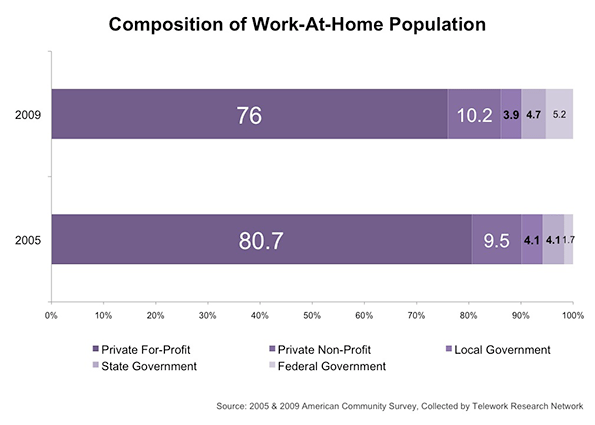
After the federal government, the next largest increase in ratio of teleworkers is at the state level. Municipal government teleworkers showed the most modest growth and represent only 3.9% among those working at home. Though only 2.4% of private for-profit sector employees consider themselves teleworkers, by size alone they represent about three-fourths of the working-at-home population.
Still, understanding of telework remains incomplete. First, as President Obama’s Council of Economic Advisors stated in 2010, there remains a persistent “lack of data on the prevalence of workplace flexibility and arrangements which makes policy-making more difficult.” There are often ambiguities such as the issue of how to distinguish between part-time and full-time teleworkers. One also must separate paid work telework (such as an official flex-time work arrangement) from non-paid telework (such as a teacher grading papers at home during the weekend). Telework’s definition is so broad that perceptions can vary dramatically.
New research attempts to bring clarity into whether employers should allow their employees to have a work-at-home option. Results from a recent study at Stanford partnered with Ctrip, an online travel-booking agency based in China, presented strong evidence to support the causal relationship between telework and productivity. With a turnover rate among Ctrip call center representatives hovering at around 50% per year (typical of the industry in China), retaining workers was a core objective of the experiment. Estimates by management say the typical costs of hiring and training a new representative is $2000, approximately 6 months of salary for an average employee.
Despite initial doubt, the research provides stark insight on efficiency gains from telecommuting gains. An article from Slate summarizes the findings:
Over the duration of the experiment, home workers answered 15 percent more calls, partly because each hour was 4 percent more productive, and partly because home office employees spent 11 percent more time answering phone calls. (Home workers took fewer breaks and sick days, rarely arrived late to their desks, and had fewer distractions.) … distractions of home life had no impact on the quality of service: The home-work group converted phone calls into sales at exactly the same rate as those in the office. And employees themselves liked the arrangement better… [and] reported less “work exhaustion,” a more positive attitude towards their jobs, and were nearly 50 percent less likely to say they were planning to quit at the end of the eight months.
In the long run, telecommuting could generate massive changes in urban geography. As benefits of telework manifest in new research, city planners ought to observe how its impact on the geography of American cities.
Teleworkers are more likely than not to live in the suburbs. Since teleworkers are often required to be tech-savvy with the latest mobile devices, one could expect a disproportionately high percentage of them working in hi-tech industries in sprawled tech hubs like the Silicon Valley. Most teleworkers choose to commute for a very practical reason: it would save them time and money. According to research by Kate Lister and Tom Harnish of the Telework Research Network, aside from housing preference the typical teleworker is a 49-year-old, college-educated, salaried, non-union employee in a management or professional role, earning $58,000 a year at a company with more than 100 employees. As of 2009, 76% of the total working-at-home population consists of the for-profit workers.
Some industries will stay clustered around the city center but more jobs, especially service-oriented ones, will continue to migrate towards the suburbs.
Teleworking will increase the total amount of hours Americans work annually. Americans, infamous for overwork, can easily translate telework as “more work.” Data from the United Nations reports 86% of American males and 67% of American females working more than 40 hours a week. While technology has often been accused as a job-killer, it has also made jobs easier and, in some ways, more social. Employers using Cloud technology are utilizing personalized social networks in hopes of creating a more connected community in the work place. The point at which work begins and leisure ends is becoming increasingly hard to distinguish as hours spent “on the job” are elusive, and thus harder to limit.
For urban planners, this signals new types of urban development to provide for a population of Americans that work longer hours but do so closer to home. Food and retail establishments will be one of the first to address this trend. Coffee shops with Wi-Fi and casual dining franchises like Panera and Corner Bakery will become commonplace in middle-to-upper class suburban neighborhoods.
These general locales could generate a privatized version of the Third Place, a milieu distinct from the two usual social environments of home and the workplace. Other urban innovations to anticipate include co-working offices, such as those offered by BLANKSPACES, and pay-as-you-go meeting services, like Liquidspace.
The availability of affordable mobile technology has been the main contributor to the "any time, any place" lifestyle. Still, the trend is limited to a small percentage of American workers, mainly those that tend to work in service-oriented positions and, as the numbers in Silicon Valley suggest, in the service sector. As more interest and funding is directed towards nanotechnology and cloud networking, perhaps this lifestyle will propagate to become the new normal. If so, telework may someday be just a common way that people work that may change forever the urban landscape.
Jeff Khau graduated from Chapman University with a degree in business entrepreneurship. Currently, he resides in Los Angeles where he is pursing his dual-masters in urban planning and public policy at the University of Southern California.
Office or home signpost photo by Bigstock.













Nice to read your article! I
Nice to read your article! I am looking forward to sharing your adventures and experiences.
188betfun
Regardless of the prevailing
Regardless of the prevailing market conditions, real estate holds tremendous potential for investors of all types.
online paper writer