NewGeography.com blogs
California, now in the midst of a heated debate on high-speed rail, could learn a thing or two from a few small villages in England about consolidating their opposition. Residents from five villages in Oxfordshire created the Villages of Oxfordshire Opposing HS2 (High-Speed Rail 2) action group to voice their concerns about the proposed project.
HS2 would link London and Birmingham by 2025, going through Finmere, Mixbury, Fingford, Fulwell, and Newton Purcell in north Oxfordshire. Not only would the rail line greatly alter the countryside landscape, but it would also create an immense amount of noise pollution. Trains would run through these villages at 250 mph about every three minutes. On top of that, rail authorities are giving out little information to citizens who are growing frustrated.
The Chairman of Villages of Oxfordshire Opposing HS2, Bernie Douglas, wants the group to influence rail authorities to route the line away from the area and raise awareness about the detriments of a high-speed rail line in the countryside. He has certainly succeeded in the latter goal. The group’s meeting in April drew more than 80 people from an area with only 100 homes. However, their efforts for the former cause have been largely in vain. Transport Minister Phillip Hammond and HS2 Ltd, the company behind the project, have not responded to the group's letters.
There is hope for Oxfordshire, though. A spokesman for the Department of Transport claims that “No final decision will be made on whether to proceed with a high-speed rail line or on its route until any scheme has undergone a full public consultation.” If this is true, it is almost certain that the rail line will not run through Oxfordshire.
Cities on the Peninsula have similarly started to band together to oppose the California Rail Authority, who has decided against using the much preferred trench system to cut costs, but opposition remains scattered throughout many different groups. Lawsuits from a few cities and organizations have driven the authority to reconsider the trench system, but the project seems like it will continue to progress, much to the dismay of many unhappy California residents.
Palo Alto, Menlo Park, and Atherton, who are at the forefront of the opposition, need to gather support from other cities on the Peninsula to truly affect the future of high-speed rail in the state. It is easy for the California Rail Authority, backed by Governor Schwarzenegger, to defend its position from a few cities, but a united Peninsula coalition would be a tough obstacle to overcome. Maybe Burlingame, San Mateo, and their neighbors should take a page out of the book of Oxfordshire and use collective action to more effectively voice their concerns.
The Age (Melbourne) headlined a story "CBA Accused of Choosing its Facts." CBA is the Commonwealth Bank of Australia, while UBS is the Swiss investment house. Commonwealth produced a report comparing housing affordability in Australian metropolitan areas to international metropolitan areas (Australian Housing and Mortgages: CBA Mortgage Book Secure). According to The Age:
Investment forums and housing blogs were alive with talk yesterday that an 18-page presentation used by the bank had replaced unfavourable housing affordability figures with data showing housing costs were not out of step with other cities in the world.
One slide compared Australian housing affordability to several cities, citing figures from a combination of the US urban planning research house Demographia and the investment bank UBS.
The slide showed housing in Sydney and Melbourne was more affordable than cities such as San Francisco, New York and Vancouver. But it used UBS data exclusively for the Australian cities, and Demographia data for the overseas cities.
The data were not comparable. Commonwealth relied upon Median Multiple data (median house price divided by median household income) from the 6th Annual Demographia Housing Affordability Survey for international metropolitan areas. However, Commonwealth used a median/average multiple (median house price divided by average household income) calculated by UBS, the Swiss investment house, for Australian metropolitan areas. These are very different indicators.
There would have been nothing wrong with having used the median/average multiple, had it been shown for all metropolitan areas, Australian and international. However, comparing the median/average multiple to the Median Multiple is invalid. Average household incomes are routinely higher than median household incomes and the use of an average income figure inappropriately biases Australian housing affordability relative to international metropolitan areas.
For example, the UBS median/average multiple for Sydney is reported by Commonwealth to be 6.2. Commonwealth finds Sydney to be more affordable than San Francisco's, which it indicates at 7.0. However, the San Francisco figure is the Median Multiple and the comparable figure for Sydney is 9.1, making Sydney less affordable than San Francisco
In fact, had the UBS median/average multiple been used for all metropolitan areas, including the international metropolitan areas, it is likely that the gap between Australian metropolitan areas and international metropolitan areas would be of similar magnitude to that shown in the Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey.
From time to time, various interests have suggested alternate measures of housing affordability for Australia and then compared or suggested comparison to our Median Multiple data. Of course, that is invalid.
The Age article by Eric Johnston was carried in other Fairfax Media outlets such asThe Sydney Morning Herald and the Brisbane Times, and the subject has been covered by financial blogs.
Note: Author Wendell Cox of Demographia.com and Hugh Pavletich of PerformanceUrbanPlanning.com are co-authors of the Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey.
The Transit Equity Network has just published a study called More Transit - More Jobs in which it suggests switching 50% of highway funding to transit in 20 metropolitan areas to create an additional 180,000 jobs over the next five years. Their basic thesis is that each kajillion in spending can produce more jobs in transit than in highways. We don't comment on that, because, frankly, the purpose of transportation spending is neither to create transit jobs nor highway jobs.
We spend on transit and highways because of benefits that extend beyond any direct employment. And, the extent of those benefits cannot be compared between the two modes. At current rates of spending each billion dollars spent on highways supports about 25 times as much personal mobility as one spent on transit. Beyond that, highway spending supports the movement of more than 1.25 billion ton miles of truck freight, which keeps product prices low and supports our affluent life style. Transit carries 0.0 ton miles of freight. Researchers such as Prud'homme & Chang-Wong and Hartgen & Fields have shown that the type of ubiquitous mobility provided by road systems produce greater economic growth. Moving money out of roads would increase traffic congestion, destroy jobs and increase product prices by slowing down trucks.
Why, on earth, then would anyone make such a dubious proposal? To paraphrase Bill Clinton, "It's the ideology, stupid." As we wrote within the past week, much of transportation spending over the last 25 years has been solidly based in an anti-mobility ideology that has produced virtually nothing in return. Already, transit, which accounts for one percent of national travel and no freight movement, accounts for more than 20% of spending on highways and transit combined. Things would be better if that were raised to 60%?
If the Transit Equity Network were right (which it is not), then why stop at 50% for transit? Why not take all of the transit and highway money and just employ people to dig holes with shovels and then fill them up again. The only costs would be wages, benefits, shovels and administration. We could save money by not buying concrete, rails, fancy trains or palatial administrative buildings. Another advantage is that the holes would require no longer term operating subsidies.
So, we need to do more than dump the ideology. We need also to dump the stupidity. Government does not exist for the purpose of government services and transportation programs do not exist for the good of transportation employees or vendors. Each dollar of infrastructure expenditures should be used to facilitate the greatest economic benefit throughout society as a whole, not just among people employed in transit (or highways for that matter).
American and European planners have long sought to improve the "jobs-housing" balance, seeking to place residents and jobs within walking or cycling distance. Of course, planners don't place people anywhere. Not surprisingly, their efforts have largely failed, from the new towns of the London area, where people travel about as far to work as anywhere else, to fabled failures of Stockholm, where high rise housing close to suburban employment centers now houses migrants who tend to have far lower incomes than native Swedes.
In the time of Mao Zedong, China had achieved perhaps the ultimate in the jobs-housing balance. Companies provided housing for their workers, who were able to walk to their jobs in the same compound. However, the economic reforms instituted by Deng Xiaoping and his successors has led to an abandonment of this model (Danwei housing) and millions of Chinese households have been lifted out of poverty into affluence. Most Chinese households do not aspire to "living on top" of the factory or office. and his successors has led to an abandonment of this model (Danwei housing) and millions of Chinese households have been lifted out of poverty into affluence. Most Chinese households do not aspire to "living on top" of the factory or office.
Foxconn (Hon Hai Precision Industry), one of the world's largest companies, is among the last to provide large amounts of housing to its workers. In its Shenzhen "Long Hua Campus," which covers only one square mile, Foxconn employs 450,000 people (Figure). They are housed on the campus or nearby in company provided units.
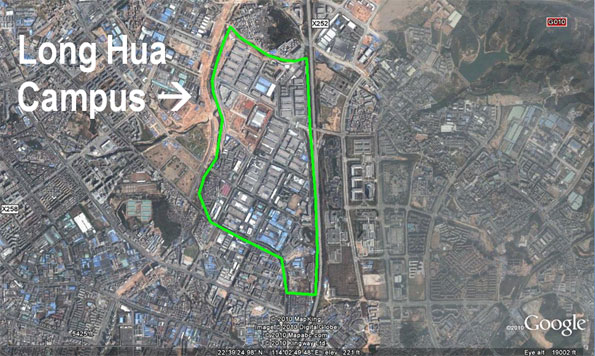
Shenzhen directly borders Hong Kong and Dongguan, which borders the Guangzhou-Foshan urban area. All together, these contiguous Pearl River Delta urban areas, along with others down the western shore to Macao have nearly 50 million people, more than live in any geographic area of the same size anywhere else in the world. These Guangdong province urban areas, along with the special economic regions of Hong Kong and Macau have become one of the world's leading manufacturing and export areas. Shenzhen itself has been estimated to have a population of between 10 million and 15 million, depending on how the migrant workers are estimated. Shenzhen and other major manufacturing centers of China are estimated to house as many as 200 millions migrants from other parts of China (especially rural areas), coming to work in jobs that pay far higher wages than can be earned at home.
 Foxconn itself is the world's largest manufacturer of consumer electronic technology, producing Apple's I-Pod and I-Phone and making products for Dell, Hewlett-Packard, Sony, as well as the Nintendo, Wii entertainment systems. Foxconn itself is the world's largest manufacturer of consumer electronic technology, producing Apple's I-Pod and I-Phone and making products for Dell, Hewlett-Packard, Sony, as well as the Nintendo, Wii entertainment systems.
According to a report in The Wall Street Journal, Foxconn has plans to abandon its Danwei housing and move away from its "perfect" jobs-housing balance to the spatial arrangements that Chinese, Americans and Europeans routinely choose --- to work where they like and live where they like.
Foxconn has had its share of difficulties. There have been the multiple employee suicides at the Long Hua Campus. The company has faced rising costs in its Pearl River Delta operations, including higher wage costs. In its attempt to retain competitiveness, Foxconn is seriously rethinking its business model and appears likely not only get out of the housing business, but will also move many of its operations into central and western China, where costs and wages are lower. This also makes sense in relation to government policy, which seeks to develop the center and west.
Overall, Taiwan headquartered Foxconn employs 920,000 people in China, the equivalent of the entire work force in the Portland or Kansas City metropolitan areas.
Foxconn plans to increase its workforce in China from 920,000 to 1,300,000 and intends for many of its employees to be in new facilities in places like Chengdu (capital of Sichuan), Wuhan (capital of Hubei), Zhengzhou (capital of Henan) and Chongqing (capital of the provincial level Chongqing municipality). Foxconn's decentralization, and the location of other new and expanded businesses in the center and west is strongly supported by China's substantial infrastructure investment. The nation already has more than 40,000 miles of interstate equivalent highways. When all of the gaps are completed, trucks will be able to reach east coast ports from Zhengzhou or Wuhan in about days drive and little more than two days from Chongqing and Chengdu.
At the same time, corporate executives can get to Beijing, Shanghai and the Pearl River Delta and other East Coast urban areas in 2.5 hours or less through some of the world's most modern airports.
Finally, the more decentralized operations will allow the migrant workers to live much closer to their homes, rather than having to travel all the way to the East Coast. This will make more frequent visits to rural villages and families possible.
----
Photo: Wuhan (photo by author)
The Wall Street Journal notes that the London Underground (metro or subway) is on strike and that transit riders are having to find alternate ways to get around. This is of course, not good news, and the transit strikes that happen often in places like Paris and periodically in places like Los Angeles and Philadelphia are a serious impediment to transit's growth (along with spending on extravagant projects and excessive and rising operating costs).
But London is actually well prepared for this emergency. Unlike Paris, Chicago and New York (where making transit strikes illegal did not prevent one), London’s buses and underground are organized in a manner that provides riders with an alternative.
The key is competitive tendering (competitive contracting) of bus service. One of the Thatcher government's most successful reforms was its reorganization of transit in London. It began in 1985, when a small part of the world's largest public bus system was put out to competitive bid. London Transport retained control of the schedules, fares, logos and bus liveries, so that the now privately operated services were an integral part of the system. Riders did not know the difference between the public and private services, until a few years later when the privately operated services began achieving better service reliability than the public services.
By 2000, the entire London bus system had been converted to competitive tendering, with multiple contractors providing the service. Costs per mile dropped by 50%, adjusted for inflation, while service was expanded and ridership rose. Regrettably, some of the efficiency gains were lost once Ken Livingstone assumed the mayorality of the new Greater London Council, while Transport for London (the successor to London Transport) failed to pay sufficient attention to retaining economic competitiveness between the contractors. Still, things are far better today than they were 25 years ago.
This competitively tendered bus system makes it possible for underground riders to get to their destinations by bus, albeit somewhat more slowly.
 Having an alternative is crucial. I recall that in response to a Southern California Rapid Transit District (SCRTD) bus strike (Note), I asked the Torrance and Gardena bus operations to "open their doors" as they traveled through low-income south central Los Angeles on their way to downtown (regulatory restrictions required them to operate in "closed door more" so as not to compete with the services of the larger Southern California Rapid Transit District). It was not long before one of my fellow Los Angeles County Transportation Commission members complained to Mayor Bradley (who had appointed me), which resulted in my withdrawal of the request. My colleague had been more concerned about the good of already well compensated transit employees to a greater extent than south central Los Angeles residents who relied on the buses for their livelihood (granted, this geographic area was outside the electoral constituency of the member). Having an alternative is crucial. I recall that in response to a Southern California Rapid Transit District (SCRTD) bus strike (Note), I asked the Torrance and Gardena bus operations to "open their doors" as they traveled through low-income south central Los Angeles on their way to downtown (regulatory restrictions required them to operate in "closed door more" so as not to compete with the services of the larger Southern California Rapid Transit District). It was not long before one of my fellow Los Angeles County Transportation Commission members complained to Mayor Bradley (who had appointed me), which resulted in my withdrawal of the request. My colleague had been more concerned about the good of already well compensated transit employees to a greater extent than south central Los Angeles residents who relied on the buses for their livelihood (granted, this geographic area was outside the electoral constituency of the member).
It is well to remember the less than sage views of Herbert Morrison, Deputy Prime Minister to Clement Atlee in the United Kingdom in the late 1940s. Morrison, the founder of the publicly operated London Transport opined that conversion of privately operated services to publicly operated services would be more efficient and better serve the public because public employees would be driven by an ethic of public service. While Nobel Laureate James Buchanan and the public choice school of economics put an academic end to such muddled thinking, London Underground's workers are in the process of providing even more tangible evidence.
----
Note: SCRTD was the operating predecessor to the current Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Association. The board on which I served, the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission was the policy predecessor.
---
Photograph by the Author
|

 Having an alternative is crucial. I recall that in response to a Southern California Rapid Transit District (SCRTD) bus strike (Note), I asked the Torrance and Gardena bus operations to "open their doors" as they traveled through low-income south central Los Angeles on their way to downtown (regulatory restrictions required them to operate in "closed door more" so as not to compete with the services of the larger Southern California Rapid Transit District). It was not long before one of my fellow Los Angeles County Transportation Commission members complained to Mayor Bradley (who had appointed me), which resulted in my withdrawal of the request. My colleague had been more concerned about the good of already well compensated transit employees to a greater extent than south central Los Angeles residents who relied on the buses for their livelihood (granted, this geographic area was outside the electoral constituency of the member).
Having an alternative is crucial. I recall that in response to a Southern California Rapid Transit District (SCRTD) bus strike (Note), I asked the Torrance and Gardena bus operations to "open their doors" as they traveled through low-income south central Los Angeles on their way to downtown (regulatory restrictions required them to operate in "closed door more" so as not to compete with the services of the larger Southern California Rapid Transit District). It was not long before one of my fellow Los Angeles County Transportation Commission members complained to Mayor Bradley (who had appointed me), which resulted in my withdrawal of the request. My colleague had been more concerned about the good of already well compensated transit employees to a greater extent than south central Los Angeles residents who relied on the buses for their livelihood (granted, this geographic area was outside the electoral constituency of the member).











